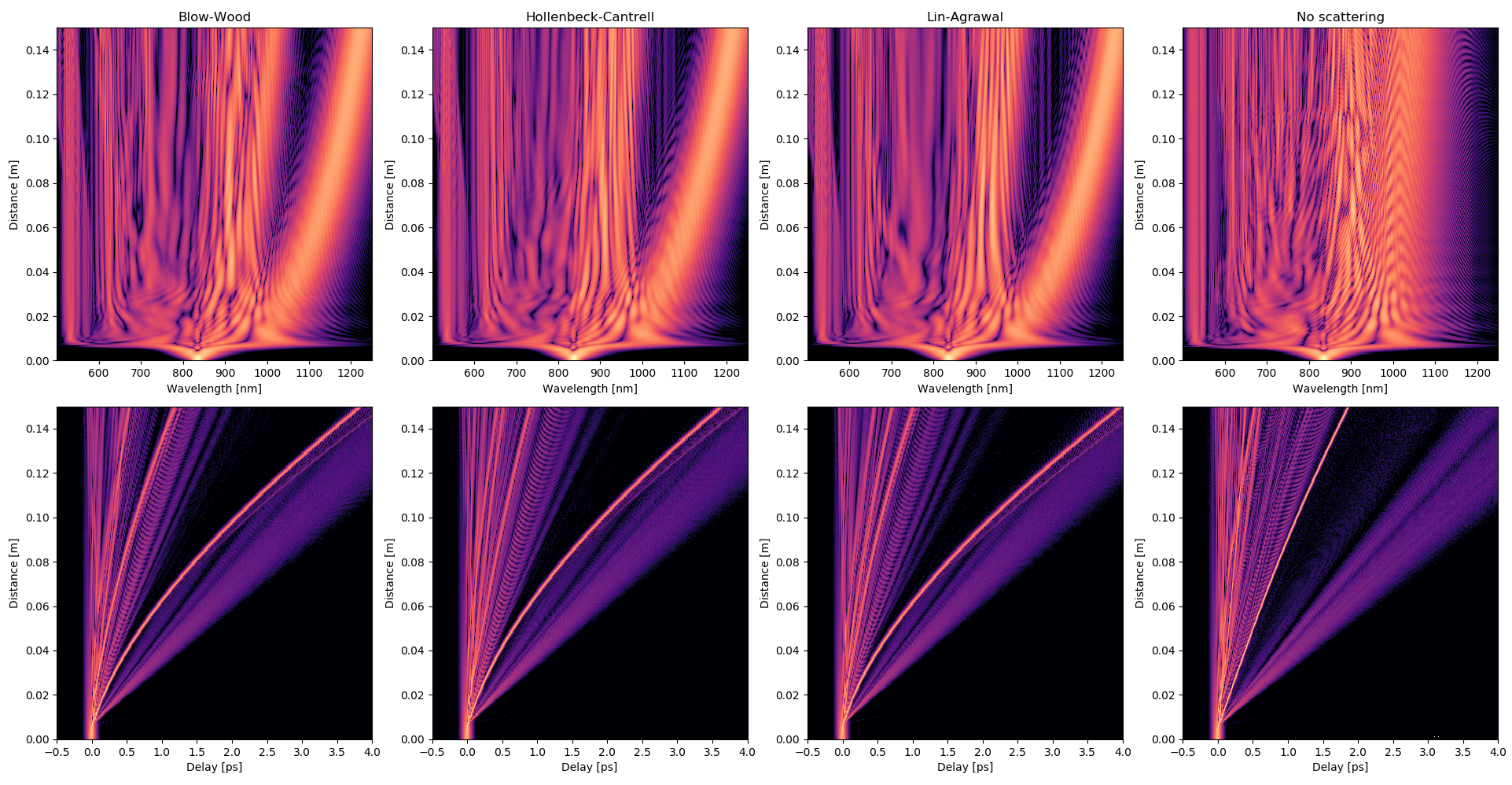
Dispersive wave generation in anomalous dispersion regime¶
Example of dispersive wave generation in anomalus dispersion regime at a central wavelength of 835 nm in a 15 centimeter long photonic crystal fiber using three different models to model Raman response.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import gnlse
if __name__ == '__main__':
setup = gnlse.GNLSESetup()
# Numerical parameters
setup.resolution = 2**14
setup.time_window = 12.5 # ps
setup.z_saves = 400
# Input pulse parameters
peak_power = 10000 # W
duration = 0.050284 # ps
# Physical parameters
setup.wavelength = 835 # nm
setup.fiber_length = 0.15 # m
setup.nonlinearity = 0.11 # 1/W/m
setup.pulse_model = gnlse.SechEnvelope(peak_power, duration)
setup.self_steepening = True
# The dispersion model is built from a Taylor expansion with coefficients
# given below.
loss = 0
betas = np.array([
-11.830e-3, 8.1038e-5, -9.5205e-8, 2.0737e-10, -5.3943e-13, 1.3486e-15,
-2.5495e-18, 3.0524e-21, -1.7140e-24
])
setup.dispersion_model = gnlse.DispersionFiberFromTaylor(loss, betas)
# This example extends the original code with additional simulations for
# three types of models of Raman response and no raman scattering case
raman_models = {
'Blow-Wood': gnlse.raman_blowwood,
'Hollenbeck-Cantrell': gnlse.raman_holltrell,
'Lin-Agrawal': gnlse.raman_linagrawal,
'No scattering': None
}
count = len(raman_models)
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10), facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
for (i, (name, raman_model)) in enumerate(raman_models.items()):
setup.raman_model = raman_model
solver = gnlse.GNLSE(setup)
solution = solver.run()
plt.subplot(2, count, i + 1)
plt.title(name)
gnlse.plot_wavelength_vs_distance(solution, WL_range=[500, 1250])
plt.subplot(2, count, i + 1 + count)
gnlse.plot_delay_vs_distance(solution, time_range=[-.5, 5])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output: