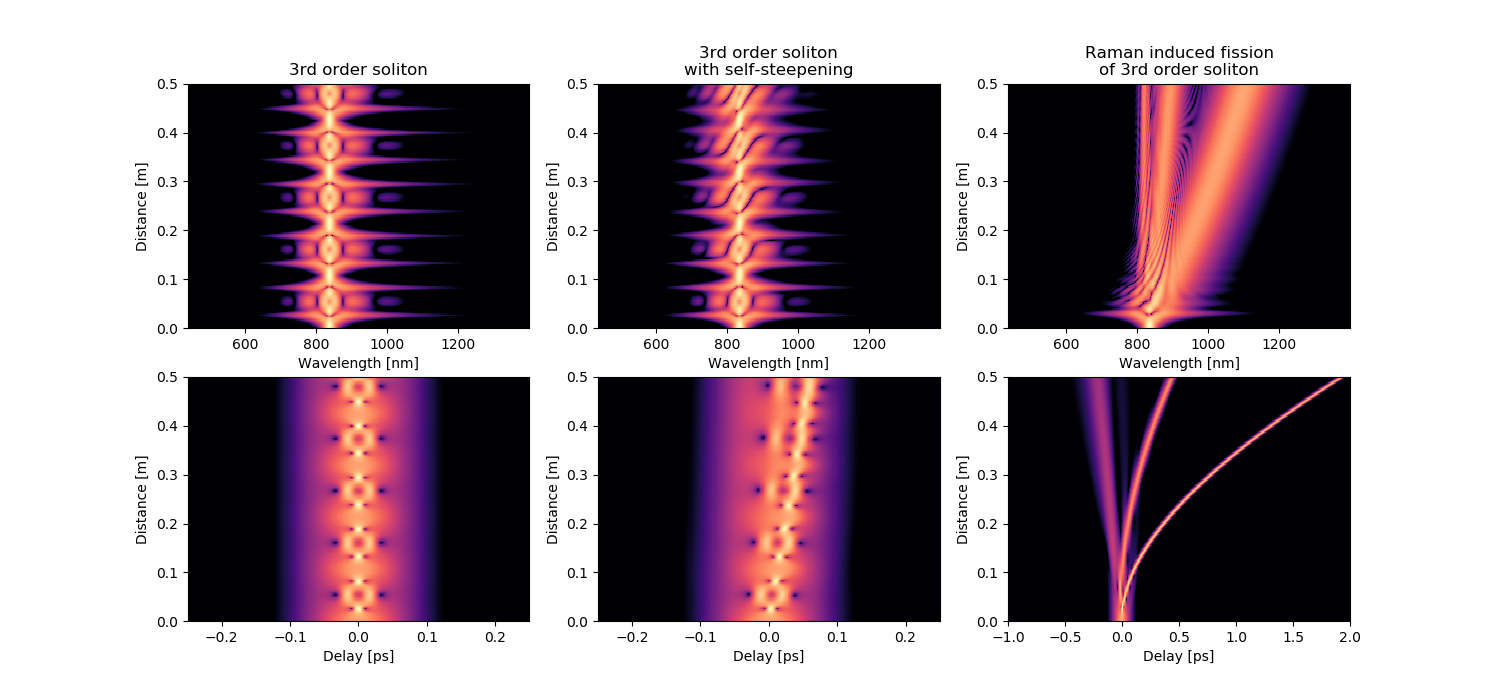
Propagation of higher-order soliton¶
Evolution of the spectral and temporal characteristics of the higher-order N = 3 soliton in three cases: - propagation without self steppening and Raman response; - soliton fission with self steppening, but no Raman response accounted; - soliton fission with self steppening, and Raman response accounted.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import gnlse
if __name__ == '__main__':
setup = gnlse.gnlse.GNLSESetup()
# Numerical parameters
# number of grid time points
setup.resolution = 2**13
# time window [ps]
setup.time_window = 12.5
# number of distance points to save
setup.z_saves = 200
# relative tolerance for ode solver
setup.rtol = 1e-6
# absoulte tolerance for ode solver
setup.atol = 1e-6
# Physical parameters
# Central wavelength [nm]
setup.wavelength = 835
# Nonlinear coefficient [1/W/m]
setup.nonlinearity = 0.11
# Dispersion: derivatives of propagation constant at central wavelength
# n derivatives of betas are in [ps^n/m]
betas = np.array([-11.830e-3])
# Input pulse: pulse duration [ps]
tFWHM = 0.050
# for dispersive length calculation
t0 = tFWHM / 2 / np.log(1 + np.sqrt(2))
# 3rd order soliton conditions
###########################################################################
# Dispersive length
LD = t0 ** 2 / np.abs(betas[0])
# Non-linear length for 3rd order soliton
LNL = LD / (3 ** 2)
# Input pulse: peak power [W]
power = 1 / (LNL * setup.nonlinearity)
# Length of soliton, in which it break dispersive characteristic
Z0 = np.pi * LD / 2
# Fiber length [m]
setup.fiber_length = .5
# Type of pulse: hyperbolic secant
setup.pulse_model = gnlse.SechEnvelope(power, 0.050)
# Loss coefficient [dB/m]
loss = 0
# Type of dyspersion operator: build from Taylor expansion
setup.dispersion_model = gnlse.DispersionFiberFromTaylor(loss, betas)
# Set type of Ramman scattering function and selftepening
simulation_type = {
'3rd order soliton': (False, None),
'3rd order soliton\nwith self-steepening': (True, None),
'Raman induced fission\nof 3rd order soliton': (True,
gnlse.raman_blowwood)
}
count = len(simulation_type)
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 7), facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
for (i, (name,
(self_steepening,
raman_model))) in enumerate(simulation_type.items()):
setup.raman_model = raman_model
setup.self_steepening = self_steepening
solver = gnlse.GNLSE(setup)
solution = solver.run()
plt.subplot(2, count, i + 1)
plt.title(name)
gnlse.plot_wavelength_vs_distance(solution, WL_range=[400, 1400])
plt.subplot(2, count, i + 1 + count)
gnlse.plot_delay_vs_distance(solution, time_range=[-.25, .25])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output: